Lumpy Skin Disease is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects cattle. This disease has garnered significant attention due to its potential to devastate livestock populations. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of Lumpy Skin Disease on the research conducted by Chughtai Lab, including its causes, symptoms, prevention, and management.
Introduction
Lumpy Skin Disease, caused by the Neethling virus, is characterized by the formation of nodules on the skin, mucous membranes, and internal organs of cattle. It is known to affect domestic and wild ruminants, with a significant impact on cattle farming.
2. The Causes of Lumpy Skin Disease
The Neethling virus belongs to the Capripoxvirus genus and is transmitted primarily through blood-feeding arthropods, such as mosquitoes and ticks. Understanding its causes is crucial to preventing its spread.
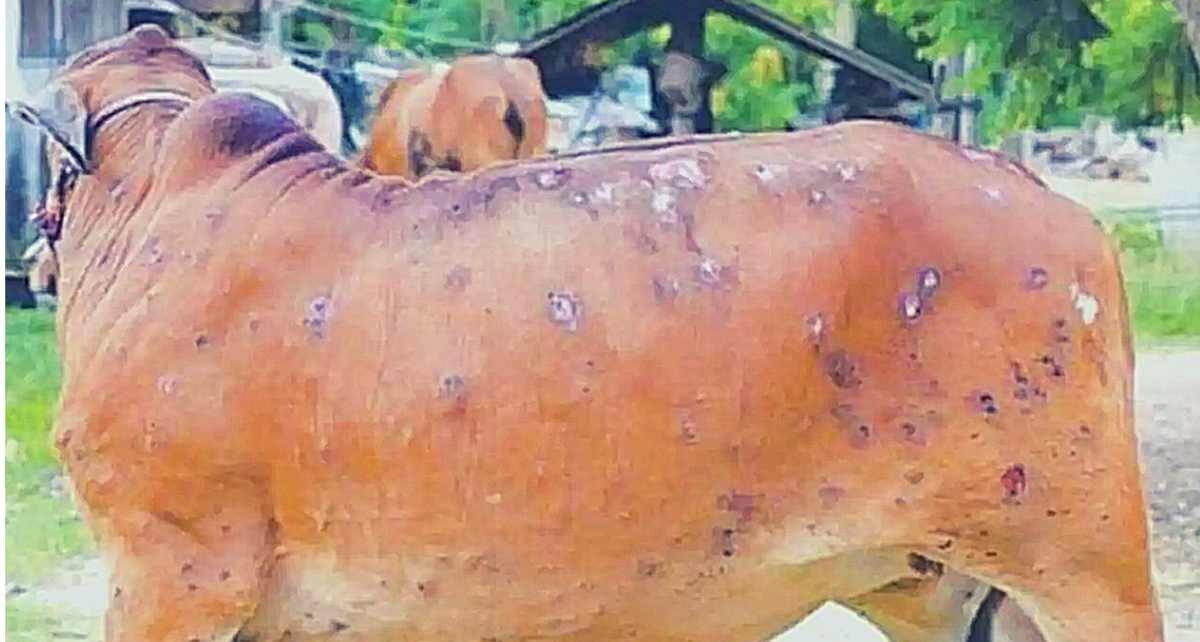
3. Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Lumpy Skin Disease manifests through various clinical signs, including fever, nasal discharge, and, most prominently, the development of nodules on the skin. These symptoms can be distressing for both the animals and farmers.
4. Geographic Distribution
Lumpy Skin Disease was initially confined to Africa but has now spread to other continents, making it a global concern. We’ll explore the regions affected and its potential for further spread.
5. Lumpy Skin Disease in Livestock
Cattle, the most susceptible hosts, suffer reduced milk production, weight loss, and decreased fertility when infected with Lumpy Skin Disease. Understanding its impact on livestock is essential for farmers.
6. Transmission and Spread
The mode of transmission plays a vital role in the rapid spread of the disease. We’ll discuss how the virus moves from one animal to another and between herds.
7. Preventive Measures
Preventing Lumpy Skin Disease is essential, as there is no specific treatment once an animal is infected. We’ll explore the biosecurity measures that can be taken on farms.
8. Vaccination Strategies
Vaccination is a crucial tool in controlling Lumpy Skin Disease. We’ll delve into the available vaccines and their effectiveness in preventing outbreaks. Where Chughtai Lab plays a vital role in research for the treatment of disease for the ease of farmers.
9. Lumpy Skin Disease Management
In the event of an outbreak, farmers and veterinarians need to know how to manage the disease. This section will provide insights into effective management strategies.
10. Economic Impact
Lumpy Skin Disease can have a severe economic impact on the livestock industry. We’ll discuss the financial repercussions of outbreaks and their ripple effects.
11. Research and Development
Ongoing research is vital in understanding and combating Lumpy Skin Disease. We’ll explore the latest advancements in the field.
12. Recent Outbreaks
Examining recent outbreaks will give readers an idea of the disease’s current status and the challenges faced in controlling it.
13. Lumpy Skin Disease vs. Other Animal Diseases
Comparing Lumpy Skin Disease to other animal diseases will help to distinguish its unique characteristics.
14. Lumpy-skin disease harmful to humans
Lumpy Skin Disease, caused by the Nettling virus, primarily affects cattle and related ruminants. However, thorough research conducted by research laboratories like Chughtai Lab and government bodies it is important to note that this disease is not harmful to humans. Lumpy Skin Disease is specific to animals and does not pose a direct health threat to people. The virus responsible for the disease does not cross the species barrier, and humans are not susceptible to infection. Therefore, while it can be devastating for livestock, especially cattle, it does not harm human populations.
15. Sum-Up
Lumpy Skin Disease is a formidable threat to livestock worldwide. Vigilance, prevention, and collaboration are essential to control and ultimately eliminate this disease. Nettling Vaccine proven for controlling Lumping skin disease in local bodies plays a huge role in the development of this vaccine like Chughtai lab and others although they are not for vets but take part in it to save animals’ lives.
FAQs
1. Is Lumpy Skin Disease contagious to humans?
Lumpy Skin Disease does not infect humans; it is specific to cattle and related animals.
2. Can Lumpy Skin Disease be cured once an animal is infected?
Unfortunately, there is no specific cure for Lumpy Skin Disease. Prevention through vaccination is key.
3. How can I protect my cattle from Lumpy Skin Disease?
Implement strict biosecurity measures and consider vaccination to protect your cattle from this disease.
4. Are there any global organizations working to combat Lumpy Skin Disease?
Yes, several organizations, such as the FAO and OIE, are actively involved in Lumpy Skin Disease control programs.
5. What should I do if I suspect Lumpy Skin Disease in my cattle?
Contact a veterinarian immediately for diagnosis and guidance on the next steps to take.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lumpy Skin Disease is a growing concern in the livestock industry. Understanding its causes, prevention, and management is essential for farmers and veterinarians. By taking the necessary precautions and staying informed, we can work together to combat this threat to cattle health and global food security.